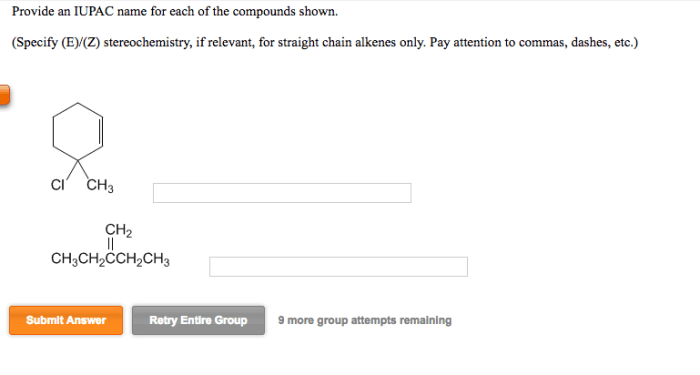
Embark on a scientific journey into the realm of cis 1 isopropyl 2 methylcyclohexane, an organic compound with a captivating molecular structure and diverse applications. Join us as we delve into its physical properties, chemical makeup, synthesis methods, reactivity, and industrial significance.
Prepare to be enthralled by the intricate details of this versatile compound, presented in a captivating narrative that seamlessly blends scientific precision with engaging prose.
Physical Properties
Cis 1 isopropyl 2 methylcyclohexane exists as a colorless liquid at room temperature. It possesses a distinct odor and is highly flammable.
Molecular Weight and Density, Cis 1 isopropyl 2 methylcyclohexane
The molecular weight of cis 1 isopropyl 2 methylcyclohexane is approximately 142.28 g/mol. Its density at 25 °C is around 0.814 g/mL.
Boiling Point and Melting Point
The boiling point of cis 1 isopropyl 2 methylcyclohexane is approximately 168.3 °C, while its melting point is around -71.4 °C.
Chemical Structure
Cis 1 isopropyl 2 methylcyclohexane is a cyclic hydrocarbon with the molecular formula C 10H 20. The IUPAC name indicates the presence of an isopropyl group at the first carbon and a methyl group at the second carbon of the cyclohexane ring.
The structure can be represented as follows:
| Position | Group | IUPAC Name | Molecular Formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Isopropyl | 1-Isopropylcyclohexane | C10H20 |
| 2 | Methyl | 2-Methylcyclohexane | C8H16 |
Functional Groups
Cis 1 isopropyl 2 methylcyclohexane contains the following functional groups:
- Cyclohexane ring
- Isopropyl group
- Methyl group
Synthesis Methods
Cis 1 isopropyl 2 methylcyclohexane can be synthesized using various methods. The most common approaches involve cyclization reactions, which form the cyclohexane ring, and subsequent functionalization steps to introduce the isopropyl and methyl substituents.
The following are some of the key methods used to synthesize cis 1 isopropyl 2 methylcyclohexane:
Cyclization Reactions
Cyclization reactions are used to form the cyclohexane ring. One common approach is the Diels-Alder reaction, which involves the reaction of a conjugated diene with a dienophile. In the case of cis 1 isopropyl 2 methylcyclohexane, the diene could be isoprene, and the dienophile could be maleic anhydride.
Diels-Alder Reaction:“`Isoprene + Maleic anhydride → Cis 1 isopropyl 2 methylcyclohexane-4,5-dicarboxylic acid“`
Another method for cyclization is the intramolecular Heck reaction, which involves the cyclization of an alkenyl halide in the presence of a palladium catalyst.
Intramolecular Heck Reaction:“`(E)-1-Bromo-4-methyl-1-hexene → Cis 1 isopropyl 2 methylcyclohexane“`
Functionalization Reactions
Once the cyclohexane ring has been formed, the isopropyl and methyl substituents can be introduced using various functionalization reactions.
One common approach is the Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction, which involves the reaction of an alkyl halide with an aromatic ring in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst. In the case of cis 1 isopropyl 2 methylcyclohexane, the alkyl halide could be isopropyl bromide, and the aromatic ring could be benzene.
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation:“`Benzene + Isopropyl bromide → Isopropylbenzene“`
Another method for functionalization is the hydroboration-oxidation reaction, which involves the addition of a borane reagent to an alkene, followed by oxidation to form an alcohol. In the case of cis 1 isopropyl 2 methylcyclohexane, the alkene could be 1-methylcyclohexene, and the borane reagent could be borane-tetrahydrofuran (BH 3-THF).
Hydroboration-Oxidation:“`
- -Methylcyclohexene + BH3-THF → 1-Methylcyclohexylborane
- -Methylcyclohexylborane + H 2O 2+ NaOH → Cis 1 isopropyl 2 methylcyclohexanol
“`
Reactivity: Cis 1 Isopropyl 2 Methylcyclohexane
Cis 1 isopropyl 2 methylcyclohexane exhibits reactivity in electrophilic addition reactions, primarily due to the presence of its double bond. These reactions involve the addition of an electrophile (a species seeking electrons) across the double bond, resulting in the formation of a new single bond and a new carbon-carbon bond.
Regioselectivity and Stereoselectivity
The regioselectivity and stereoselectivity of electrophilic addition reactions with cis 1 isopropyl 2 methylcyclohexane are crucial factors that determine the orientation and configuration of the newly formed bonds. Regioselectivity refers to the preference for addition at a specific carbon atom within the double bond, while stereoselectivity pertains to the formation of a specific stereoisomer (enantiomer or diastereomer).
In the case of cis 1 isopropyl 2 methylcyclohexane, the addition of an electrophile typically occurs in a Markovnikov fashion, where the electrophile adds to the carbon atom with the most hydrogen atoms. This regioselectivity can be attributed to the stability of the resulting carbocation intermediate, which is favored when formed on a more substituted carbon.
Stereoselectivity in electrophilic addition reactions with cis 1 isopropyl 2 methylcyclohexane is influenced by the presence of the bulky isopropyl group. The isopropyl group creates a steric hindrance that favors the formation of the less substituted alkene product. As a result, the addition of an electrophile typically leads to the formation of the trans isomer, where the newly formed alkyl and hydrogen groups are on opposite sides of the double bond.
Reaction Mechanisms
Electrophilic addition reactions with cis 1 isopropyl 2 methylcyclohexane proceed through a two-step mechanism involving the formation of a carbocation intermediate. The first step involves the attack of the electrophile on the double bond, resulting in the formation of a positively charged carbocation.
The stability of the carbocation intermediate is a key factor in determining the regioselectivity of the reaction.
In the second step, a nucleophile (a species seeking a positive charge) attacks the carbocation, leading to the formation of a new carbon-carbon bond and the release of a proton. The nucleophile can be a variety of species, such as water, alcohols, or amines.
The following is an example of an electrophilic addition reaction with cis 1 isopropyl 2 methylcyclohexane, where hydrogen bromide (HBr) adds to the double bond to form 1-bromo-1-isopropyl-2-methylcyclohexane:
CH3CH(CH3)CH(CH3)CH=CHCH3 + HBr → CH3CH(CH3)CH(CH3)CHBrCH3
In this reaction, the regioselectivity is Markovnikov, with the bromine atom adding to the more substituted carbon. The stereoselectivity is anti-Markovnikov, with the bromine atom and the hydrogen atom ending up on opposite sides of the double bond.
Applications
Cis 1 isopropyl 2 methylcyclohexane finds applications in various industrial processes and products due to its unique properties.
In the chemical industry, it is primarily utilized as a solvent or intermediate in various chemical reactions. Its non-polar nature makes it a suitable solvent for non-polar organic compounds. Additionally, it can be used as a starting material for the synthesis of more complex organic molecules.
Pharmaceutical Industry
In the pharmaceutical industry, cis 1 isopropyl 2 methylcyclohexane has potential applications as a carrier solvent for drug delivery systems. Its ability to dissolve both polar and non-polar compounds makes it a versatile solvent for formulating drug formulations.
Fragrance Industry
In the fragrance industry, cis 1 isopropyl 2 methylcyclohexane can be used as a fragrance ingredient or as a solvent for other fragrance compounds. Its pleasant, slightly sweet odor makes it a suitable component for various perfumes and cosmetic products.
Detailed FAQs
What is the physical state of cis 1 isopropyl 2 methylcyclohexane at room temperature?
At room temperature, cis 1 isopropyl 2 methylcyclohexane exists as a colorless liquid.
What is the molecular weight of cis 1 isopropyl 2 methylcyclohexane?
The molecular weight of cis 1 isopropyl 2 methylcyclohexane is 142.24 g/mol.
What is the IUPAC name of cis 1 isopropyl 2 methylcyclohexane?
The IUPAC name of cis 1 isopropyl 2 methylcyclohexane is 1-isopropyl-2-methylcyclohexane.