With notes 6-2 properties of parallelograms at the forefront, this discourse delves into the fascinating world of parallelograms, exploring their distinctive features and diverse applications. From their defining characteristics to their practical uses, this exploration unravels the intricate details of these geometric shapes.
Parallelograms, with their unique combination of parallel sides and congruent opposite sides, exhibit a range of properties that set them apart from other quadrilaterals. These properties include the bisection of diagonals, the formation of congruent triangles, and the relationships between their area and perimeter.
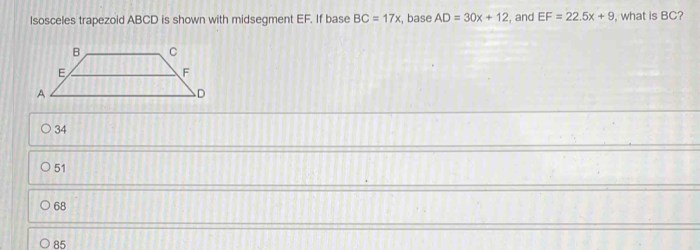
Properties of Parallelograms: Notes 6-2 Properties Of Parallelograms
Parallelograms are quadrilaterals with two pairs of parallel sides. They possess distinct characteristics that distinguish them from other quadrilaterals.
The properties of parallelograms include:
- Opposite sides are congruent (equal in length).
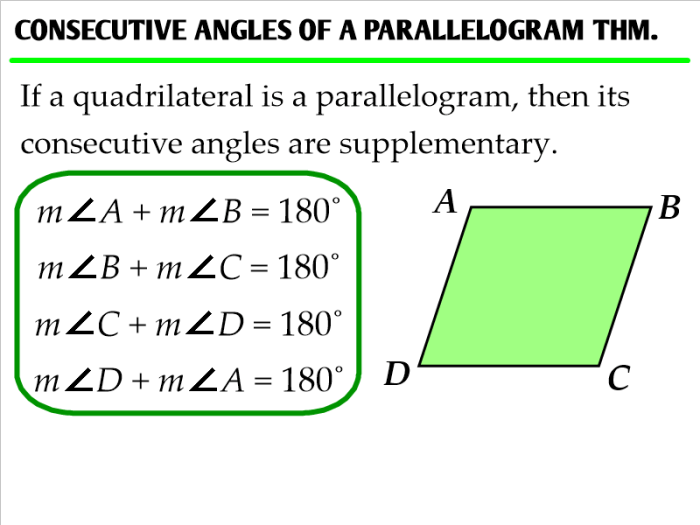
- Opposite angles are congruent.
- Diagonals bisect each other.
- Diagonals create four congruent triangles.
- The sum of the interior angles is 360 degrees.
Types of Parallelograms
There are several types of parallelograms, each with its own specific properties:
- Rectangles:Rectangles are parallelograms with four right angles.
- Squares:Squares are rectangles with four equal sides.
- Rhombuses:Rhombuses are parallelograms with four congruent sides.
Diagonals of Parallelograms, Notes 6-2 properties of parallelograms
The diagonals of a parallelogram are line segments that connect opposite vertices. They possess the following properties:
- Diagonals bisect each other at a single point.
- Diagonals create four congruent triangles.
- The diagonals divide the parallelogram into two congruent triangles.
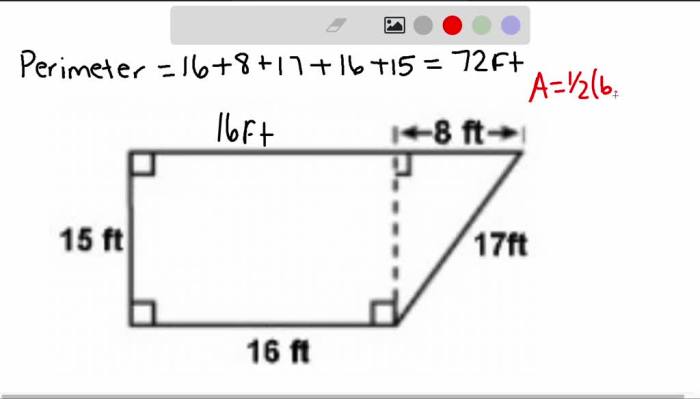
Area and Perimeter of Parallelograms
The area of a parallelogram is calculated by multiplying the base (length of one side) by the height (length of the perpendicular segment from the base to the opposite side). The formula for the area of a parallelogram is: A = b- h
The perimeter of a parallelogram is calculated by adding the lengths of all four sides. The formula for the perimeter of a parallelogram is: P = 2(b + h)
Applications of Parallelograms
Parallelograms have various practical applications in different fields:
- Architecture:Parallelograms are used in the design of buildings, bridges, and other structures.
- Engineering:Parallelograms are used in the design of machines, vehicles, and other mechanical devices.
- Design:Parallelograms are used in the design of logos, artwork, and other graphic elements.
FAQ Compilation
What are the key properties of parallelograms?
Parallelograms possess several key properties, including parallel opposite sides, congruent opposite sides, diagonals that bisect each other, and the formation of congruent triangles when diagonals intersect.
How do you calculate the area of a parallelogram?
The area of a parallelogram can be calculated using the formula: Area = base × height, where the base is the length of one side and the height is the perpendicular distance from the base to the opposite side.
What are some practical applications of parallelograms?
Parallelograms find applications in various fields, such as architecture (e.g., designing buildings with symmetrical facades), engineering (e.g., constructing bridges and trusses), and design (e.g., creating patterns and logos).