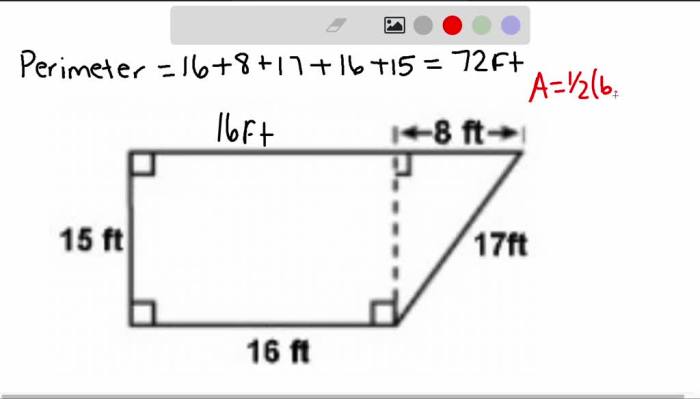
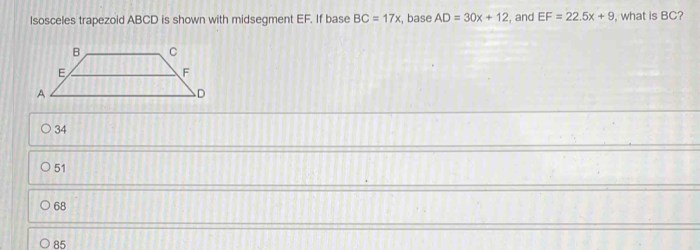
Unit 7 polygons and quadrilaterals homework 1 angles of polygons – Unit 7 Polygons and Quadrilaterals Homework 1: Angles of Polygons delves into the captivating world of polygons and quadrilaterals, exploring their angles and properties. Join us on this mathematical adventure as we uncover the fascinating relationships between these geometric shapes.
This homework assignment provides a comprehensive understanding of polygons and quadrilaterals, equipping you with the knowledge to analyze and apply these concepts in real-world applications. Prepare to be amazed as we embark on a journey through the realm of geometry.
1. Introduction to Polygons and Quadrilaterals
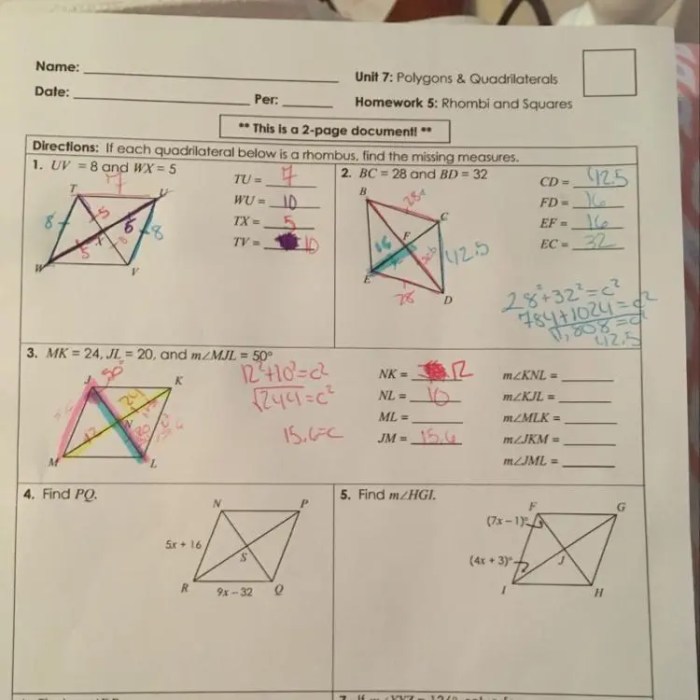
Polygons are closed figures with straight sides and angles. Quadrilaterals are polygons with four sides. Polygons can be classified by the number of sides they have, while quadrilaterals can be classified by the types of angles they have.
1.1 Types of Polygons
- Triangle: 3 sides
- Quadrilateral: 4 sides
- Pentagon: 5 sides
- Hexagon: 6 sides
- Heptagon: 7 sides
- Octagon: 8 sides
1.2 Types of Quadrilaterals
- Square: 4 equal sides and 4 right angles
- Rectangle: 4 right angles, opposite sides equal
- Rhombus: 4 equal sides, opposite angles equal
- Parallelogram: Opposite sides parallel
- Trapezoid: One pair of parallel sides
1.3 Relationship between Polygons and Quadrilaterals
All quadrilaterals are polygons, but not all polygons are quadrilaterals. A quadrilateral is a specific type of polygon with four sides.
2. Measuring Angles of Polygons
The angles of a polygon are the measures of the angles formed by the intersection of its sides. Angles can be measured in degrees, radians, or gradians.
2.1 Units of Angle Measurement
- Degrees: 1/360 of a full circle
- Radians: 1/2π of a full circle
- Gradians: 1/400 of a full circle
2.2 Measuring the Angles of a Polygon
To measure the angles of a polygon, use a protractor. Place the center of the protractor on a vertex of the polygon and align the baseline with one of the sides. Read the measure of the angle from the scale on the protractor.
3. Properties of Polygons
Polygons have certain properties that depend on the number of sides they have. These properties include the number of angles, the sum of the interior angles, and the number of diagonals.
3.1 Number of Angles and Sides
The number of angles in a polygon is equal to the number of sides.
3.2 Sum of Interior Angles, Unit 7 polygons and quadrilaterals homework 1 angles of polygons
The sum of the interior angles of a polygon with nsides is given by ( n– 2) × 180 degrees.
3.3 Number of Diagonals
The number of diagonals in a polygon with nsides is given by n( n– 3)/2.
3.4 Symmetry
Polygons can have different types of symmetry, including:
- Line symmetry
- Point symmetry
- Rotational symmetry
4. Properties of Quadrilaterals: Unit 7 Polygons And Quadrilaterals Homework 1 Angles Of Polygons
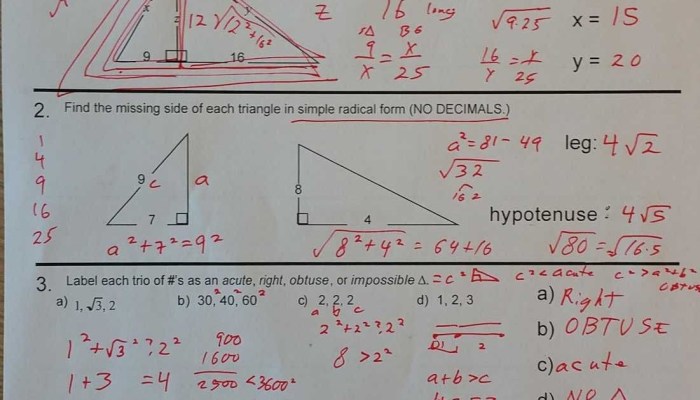
Quadrilaterals have specific properties that depend on the types of angles they have. These properties include the sum of the interior angles, the types of diagonals, and the types of symmetry.
4.1 Sum of Interior Angles
The sum of the interior angles of a quadrilateral is 360 degrees.
4.2 Types of Diagonals
Quadrilaterals can have different types of diagonals, including:
- Perpendicular diagonals
- Parallel diagonals
- Equal diagonals
4.3 Types of Symmetry
Quadrilaterals can have different types of symmetry, including:
- Line symmetry
- Point symmetry
- Rotational symmetry
5. Applications of Polygons and Quadrilaterals
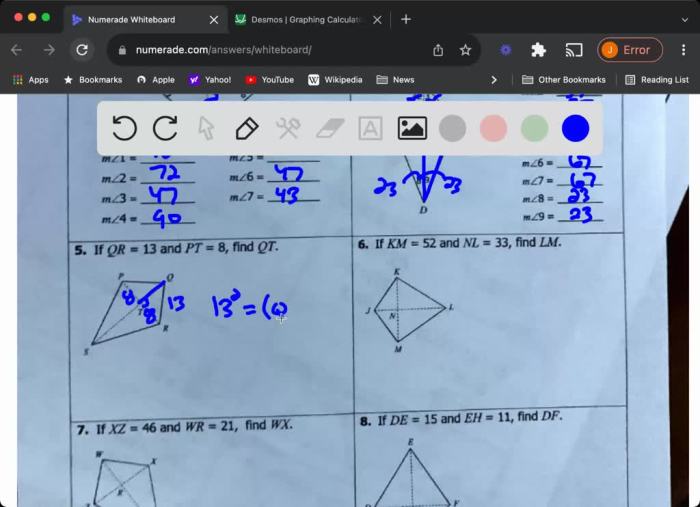
Polygons and quadrilaterals have numerous applications in various fields, including:
5.1 Architecture
Polygons and quadrilaterals are used in the design of buildings, bridges, and other structures.
5.2 Engineering
Polygons and quadrilaterals are used in the design of machines, vehicles, and other engineering structures.
5.3 Design
Polygons and quadrilaterals are used in the design of logos, graphics, and other visual elements.
Detailed FAQs
What is the definition of a polygon?
A polygon is a closed two-dimensional figure with straight sides.
What is the difference between a polygon and a quadrilateral?
A quadrilateral is a polygon with four sides, while a polygon can have any number of sides.
How do you measure the angles of a polygon?
To measure the angles of a polygon, you can use a protractor or a compass.