Inflation causes a violation of this assumption – Inflation, the persistent rise in prices, violates a fundamental assumption of constant prices in economic models, leading to distortions in decision-making and significant consequences for individuals, businesses, and the overall economy.
Inflation undermines the assumption of constant prices, which is crucial for accurate economic analysis and forecasting. When prices change over time, the purchasing power of money fluctuates, affecting consumption, investment, and savings decisions.
Inflation and its Consequences
Inflation is a persistent increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over time. It is a major economic concern as it erodes the purchasing power of money, leading to various economic distortions and consequences.
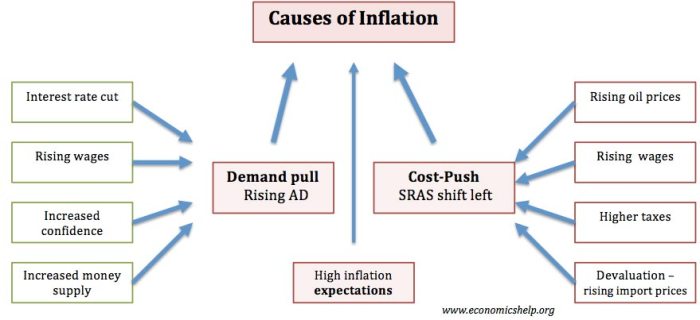
Inflation can be caused by a number of factors, including:
- Increased demand for goods and services
- Supply shortages
- Expansionary monetary policy
- Government spending
Real-world examples of inflation include the hyperinflation experienced in Germany in the early 1920s, the high inflation rates in Zimbabwe in the late 2000s, and the current inflation surge in the United States.
Violation of Assumptions
In economic models, it is often assumed that prices remain constant. However, inflation violates this assumption, as it leads to changes in the price level over time.
This violation can lead to distortions in economic decision-making. For example, if businesses expect inflation to continue, they may raise prices in anticipation, which can lead to a self-fulfilling prophecy of even higher inflation.
Inflation can also distort investment decisions. If investors expect inflation to erode the value of their returns, they may be less likely to invest, which can slow economic growth.
Consequences of Inflation
Inflation has a number of consequences for individuals and businesses:
- Reduced purchasing power:As prices rise, the value of money decreases, making it harder for people to afford the same goods and services.
- Erosion of savings:Inflation can erode the value of savings over time, as the purchasing power of the money saved declines.
- Distorted investment decisions:Inflation can make it difficult for businesses to make sound investment decisions, as they must consider the potential impact of inflation on their returns.
- Reduced economic growth:Inflation can slow economic growth by discouraging investment and consumer spending.
Mitigation Strategies, Inflation causes a violation of this assumption
There are a number of strategies that governments and central banks can use to mitigate the effects of inflation:
- Monetary policy:Central banks can use monetary policy tools, such as raising interest rates, to control inflation.
- Fiscal policy:Governments can use fiscal policy tools, such as reducing government spending or increasing taxes, to reduce inflation.
- Supply-side policies:Governments can implement supply-side policies, such as increasing the supply of goods and services, to reduce inflation.
The effectiveness of these strategies depends on the underlying causes of inflation.
Case Studies
There are a number of case studies of countries that have experienced significant inflation. These case studies can provide valuable lessons about the causes and consequences of inflation.
One example is the hyperinflation experienced in Germany in the early 1920s. This hyperinflation was caused by a combination of factors, including the reparations payments imposed on Germany after World War I and the government’s decision to finance these payments by printing money.
The hyperinflation had a devastating impact on the German economy. It led to a loss of confidence in the currency, a collapse in investment, and widespread poverty.
Detailed FAQs: Inflation Causes A Violation Of This Assumption
What is the primary assumption violated by inflation?
Inflation violates the assumption of constant prices in economic models.
How does inflation distort economic decision-making?
Inflation can lead to distortions in investment, consumption, and savings decisions due to changes in purchasing power.
What are the key consequences of inflation for individuals and businesses?
Inflation can erode purchasing power, reduce savings, and increase uncertainty in investment decisions.