Price indices and inflation worksheet answers – Welcome to the realm of price indices and inflation, where understanding these concepts is crucial for comprehending the economic landscape. This worksheet provides a comprehensive guide to unraveling the intricacies of price indices and their role in measuring inflation, equipping you with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of economic analysis and policymaking.
Delving into the intricacies of price indices, we will explore the methodologies employed to calculate them, including the significance of the “basket of goods” and the impact of weighting items within it. By deciphering the nuances of price index interpretation, we will gain insights into inflation trends and their implications for economic forecasts and policy decisions.
Overview of Price Indices and Inflation: Price Indices And Inflation Worksheet Answers
Price indices are statistical measures that track changes in the prices of goods and services over time. They are essential tools for measuring inflation, which is the rate at which the overall price level of goods and services is rising.
There are different types of price indices, including the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and the Producer Price Index (PPI). The CPI measures the change in prices paid by consumers for a basket of goods and services, while the PPI measures the change in prices received by producers for their goods and services.
Price indices are used extensively in economic analysis and policymaking. They are used to track inflation, monitor economic growth, and make decisions about interest rates and other economic policies.
Calculation of Price Indices
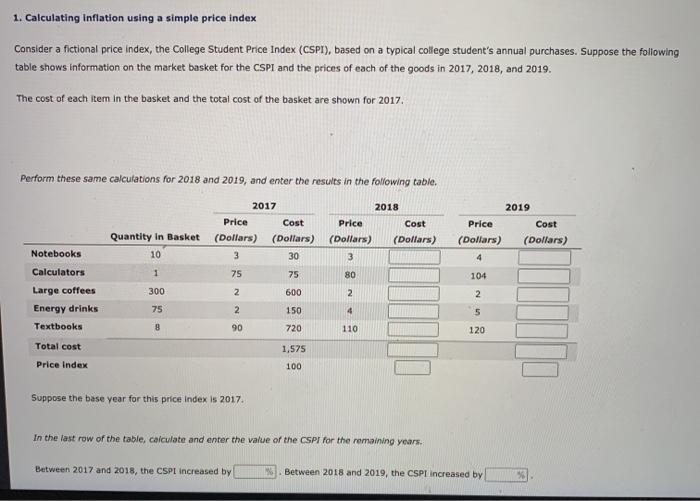
Price indices are calculated by comparing the prices of a basket of goods and services over time. The basket is a representative sample of the goods and services purchased by consumers or producers.
The items in the basket are weighted according to their importance in the overall economy. For example, the CPI weights food items more heavily than luxury items because food is a more essential part of the average consumer’s budget.
The price index is calculated by taking the average price of the items in the basket in the current period and dividing it by the average price of the same items in a base period. The result is multiplied by 100 to create an index value.
Interpretation of Price Indices, Price indices and inflation worksheet answers
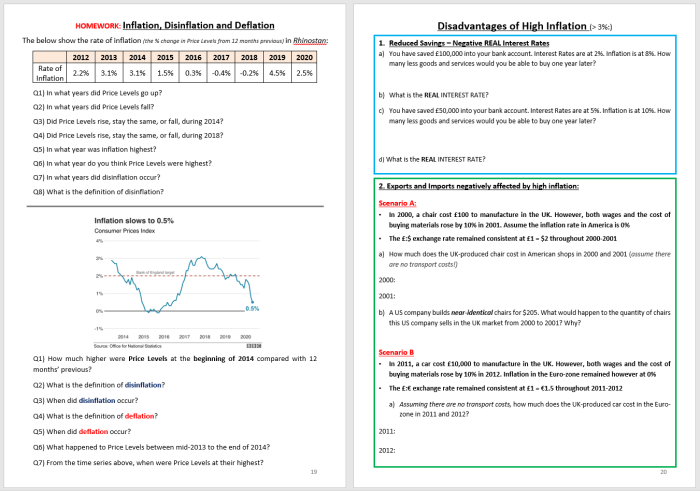
Price indices can be used to identify trends in inflation. If the price index is rising, it means that the overall price level of goods and services is increasing. Conversely, if the price index is falling, it means that the overall price level is decreasing.
Price indices can also be used to compare inflation rates across different countries or regions. For example, if the CPI in the United States is rising faster than the CPI in the European Union, it means that inflation is higher in the United States.
However, it is important to note that price indices have some limitations. They can be affected by factors such as substitution and quality changes. For example, if consumers switch to buying cheaper brands of goods, the CPI may not fully capture the true increase in the cost of living.
Inflation and Its Impact
Inflation is the sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time. It can be caused by a number of factors, including:
- Demand-pull inflation: This occurs when there is too much money chasing too few goods.
- Cost-push inflation: This occurs when the costs of production increase, such as when wages or oil prices rise.
Inflation can have a number of negative consequences, including:
- Reduced purchasing power: Inflation erodes the value of money, making it harder for people to afford the same goods and services.
- Higher interest rates: Inflation can lead to higher interest rates, which can make it more expensive to borrow money.
- Reduced economic growth: Inflation can reduce economic growth by making it more difficult for businesses to invest and expand.
Policy Responses to Inflation
There are a number of policy tools that can be used to control inflation, including:
- Monetary policy: This involves using interest rates to control the supply of money in the economy.
- Fiscal policy: This involves using government spending and taxes to influence the overall level of economic activity.
- Supply-side policies: These policies are designed to increase the supply of goods and services in the economy.
The effectiveness of these policies depends on the specific circumstances of each country or region.
FAQ Resource
What is the significance of price indices in economic analysis?
Price indices serve as essential tools for measuring inflation, tracking changes in the cost of living, and analyzing economic trends. They provide valuable insights for policymakers, businesses, and individuals alike.
How are price indices calculated?
Price indices are calculated by comparing the prices of a fixed basket of goods and services over time. The basket is carefully selected to represent the typical consumption patterns of a specific population.
What are the different types of price indices?
Common types of price indices include the Consumer Price Index (CPI), which measures changes in the prices of goods and services purchased by households, and the Producer Price Index (PPI), which tracks changes in the prices of goods sold by producers.