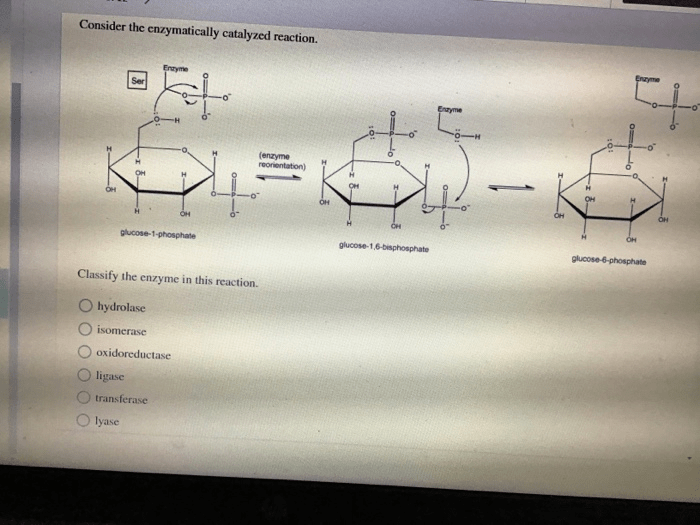
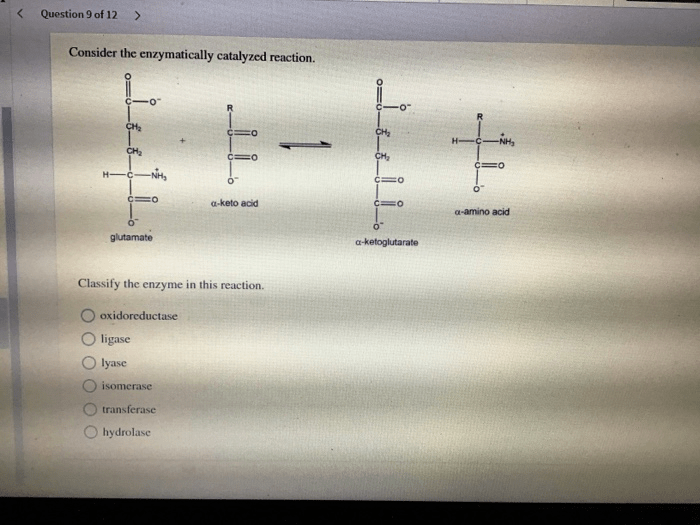
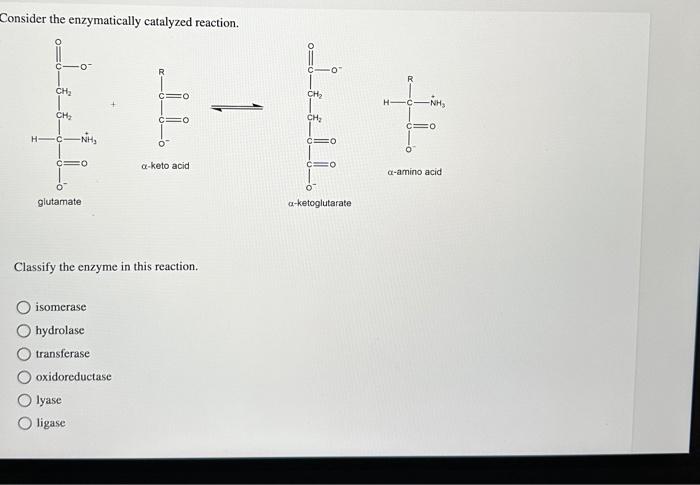
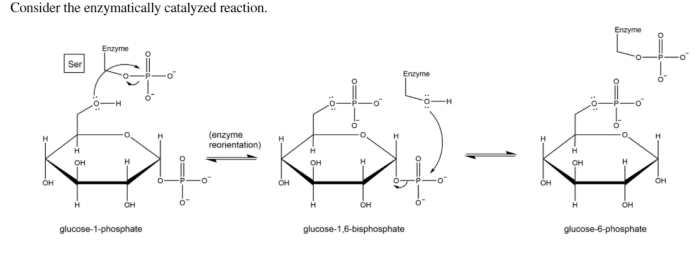
Consider the enzymatically catalyzed reaction. – Consider the enzymatically catalyzed reaction, a captivating dance of molecules where enzymes orchestrate the symphony of life. These biological maestros facilitate biochemical transformations, driving the very essence of cellular processes. Delve into their intricate world, where structure, function, and kinetics intertwine to reveal the secrets of life’s molecular machinery.
Enzymes, the master catalysts, wield their power to accelerate reactions, enabling life to flourish. Their diverse nature reflects the myriad of chemical reactions that sustain us. From digestion to DNA replication, enzymes are the unsung heroes behind the scenes, shaping our existence at the molecular level.
Enzymes and Enzymatic Reactions: Consider The Enzymatically Catalyzed Reaction.
Enzymes are biological catalysts that facilitate chemical reactions within living organisms. They are essential for the functioning of cells and the overall health of the organism. Enzymes have a specific structure that allows them to bind to a specific substrate and catalyze the reaction.
Catalyzed Reactions, Consider the enzymatically catalyzed reaction.
Enzyme catalysis is the process by which enzymes increase the rate of a reaction without being consumed. Enzymes achieve this by providing an alternative pathway for the reaction to occur, which has a lower activation energy than the uncatalyzed reaction.
The mechanisms of enzyme catalysis include electrostatic interactions, hydrogen bonding, and the formation of enzyme-substrate complexes.
Reaction Kinetics
Reaction kinetics is the study of the rates of chemical reactions. The Michaelis-Menten equation is a mathematical model that describes the relationship between the reaction rate and the substrate concentration. Enzyme inhibition is the process by which the activity of an enzyme is decreased.
There are different types of enzyme inhibition, including competitive inhibition, non-competitive inhibition, and uncompetitive inhibition.
Applications of Enzymatic Reactions
Enzymes have a wide range of industrial applications, including the production of food, beverages, and pharmaceuticals. Enzymes are also used in biotechnology, such as in the production of biofuels and the development of new drugs. In medicine, enzymes are used for diagnostic purposes and in the treatment of diseases.
Additional Considerations
Cofactors and coenzymes are molecules that are required for the activity of some enzymes. Enzyme regulation is the process by which the activity of enzymes is controlled. There are different techniques that can be used to study enzymatic reactions, including enzyme assays and kinetic studies.
Q&A
What is the role of enzymes in biological systems?
Enzymes act as catalysts, accelerating biochemical reactions essential for life processes, such as metabolism, digestion, and DNA replication.
How do enzymes catalyze reactions?
Enzymes lower the activation energy required for a reaction to occur, facilitating its progress without being consumed.
What factors affect enzyme activity?
Factors like temperature, pH, enzyme concentration, and the presence of inhibitors or activators can influence enzyme activity.
What are the applications of enzymatic reactions?
Enzymes find applications in industries (e.g., food processing, detergents), biotechnology (e.g., genetic engineering, biofuels), and medicine (e.g., diagnostics, drug development).