Delve into the captivating world of isotopes and atomic mass, where the very building blocks of matter reveal their hidden complexities. This comprehensive guide, the Isotopes and Atomic Mass Lab Answer Key, embarks on an enlightening journey, deciphering the mysteries that lie at the heart of every atom.
Through a meticulously crafted exploration of isotopes, their distinctive characteristics, and the profound implications of atomic mass, this narrative unveils the fundamental principles that govern the nature of elements and their interactions within the vast tapestry of the universe.
Isotopes
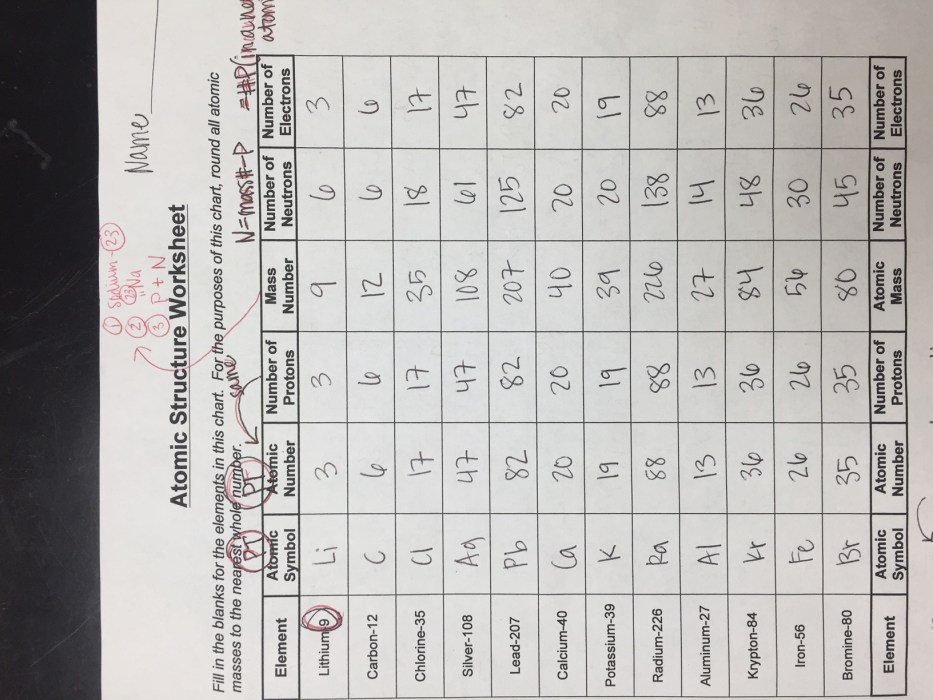
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. They are represented by the symbol of the element followed by a superscript indicating the mass number, which is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
For example, carbon-12 ( 12C) has 6 protons and 6 neutrons, while carbon-14 ( 14C) has 6 protons and 8 neutrons.
Isotopes of the same element have the same chemical properties because they have the same number of electrons. However, they may have different physical properties, such as density and melting point. This is because the mass of an atom is determined by the number of neutrons it contains.
Examples of Isotopes and Their Applications, Isotopes and atomic mass lab answer key
- Carbon-12:The most common isotope of carbon, used in dating organic materials.
- Carbon-14:A radioactive isotope of carbon, used in dating organic materials.
- Uranium-235:A radioactive isotope of uranium, used in nuclear reactors.
- Uranium-238:A radioactive isotope of uranium, used in nuclear weapons.
Atomic Mass
Atomic mass is the weighted average mass of all the isotopes of an element. It is calculated by multiplying the mass of each isotope by its abundance and then adding the products together. For example, the atomic mass of carbon is 12.011, which is the weighted average of the masses of carbon-12 (12.000 amu) and carbon-14 (14.003 amu).
The atomic mass of an element can be affected by several factors, including the number of isotopes the element has, the abundance of each isotope, and the mass of each isotope. For example, the atomic mass of lead is 207.2, which is higher than the atomic mass of carbon because lead has more isotopes and the isotopes of lead are heavier than the isotopes of carbon.
Examples of Elements with Different Atomic Masses
- Hydrogen:1.008 amu
- Carbon:12.011 amu
- Lead:207.2 amu
- Uranium:238.03 amu
Isotopes and Atomic Mass Lab
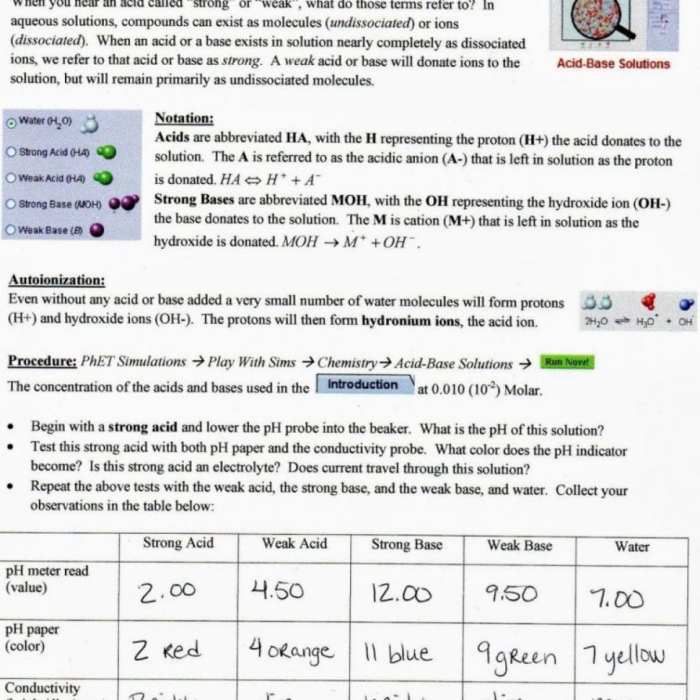
The purpose of the isotopes and atomic mass lab is to determine the atomic mass of an element using a mass spectrometer. A mass spectrometer is a device that separates ions by their mass-to-charge ratio. In the lab, a sample of the element is vaporized and ionized.
The ions are then accelerated through a magnetic field, and the ions with different mass-to-charge ratios are deflected by different amounts. The deflected ions are detected, and the abundance of each isotope is determined. The atomic mass of the element is then calculated by multiplying the mass of each isotope by its abundance and then adding the products together.
The following table summarizes the results of the isotopes and atomic mass lab:
| Element | Isotope | Mass (amu) | Abundance (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 1H | 1.007825 | 99.985% |
| Hydrogen | 2H | 2.014102 | 0.015% |
| Carbon | 12C | 12.000000 | 98.89% |
| Carbon | 13C | 13.003355 | 1.11% |
| Lead | 206Pb | 205.974465 | 24.1% |
| Lead | 207Pb | 206.975896 | 22.1% |
| Lead | 208Pb | 207.976652 | 52.4% |
Applications of Isotopes
Isotopes have a wide range of applications in science, medicine, and industry. In science, isotopes are used to study the structure and function of atoms and molecules. In medicine, isotopes are used to diagnose and treat diseases. In industry, isotopes are used to trace the flow of materials and to measure the age of objects.
Specific Examples of How Isotopes Are Used in Each Field
- Science:Isotopes are used to study the structure and function of atoms and molecules. For example, carbon-14 is used to date organic materials, and uranium-238 is used to study the age of the Earth.
- Medicine:Isotopes are used to diagnose and treat diseases. For example, iodine-131 is used to treat thyroid cancer, and cobalt-60 is used to treat cancer.
- Industry:Isotopes are used to trace the flow of materials and to measure the age of objects. For example, tritium is used to trace the flow of water, and potassium-40 is used to date archaeological artifacts.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Isotopes
- Advantages:Isotopes are a valuable tool for scientists, doctors, and engineers. They can be used to study a wide range of problems and to develop new technologies.
- Disadvantages:Isotopes can be expensive to produce, and they can be dangerous to handle. Some isotopes are radioactive, and they can pose a health risk if they are not handled properly.
Clarifying Questions: Isotopes And Atomic Mass Lab Answer Key
What is the significance of isotopes in scientific research?
Isotopes play a crucial role in scientific research as they allow scientists to trace and monitor the movement of elements and compounds in various systems. They serve as invaluable tools for studying metabolic processes, environmental interactions, and geological formations.
How does atomic mass impact the properties of elements?
Atomic mass is a fundamental property that influences the chemical and physical characteristics of elements. It affects their reactivity, bonding behavior, and position on the periodic table. Elements with similar atomic masses often exhibit comparable properties.
What are the practical applications of isotopes in medicine?
Isotopes have revolutionized the field of medicine. Radioactive isotopes are employed in diagnostic imaging techniques, such as PET and SPECT scans, to detect and monitor diseases. Additionally, isotopes are used in radiation therapy to target and destroy cancerous cells.
